| MIR STEEL
Continuous & efficient substrate dehydration with no dust generation or vibration.
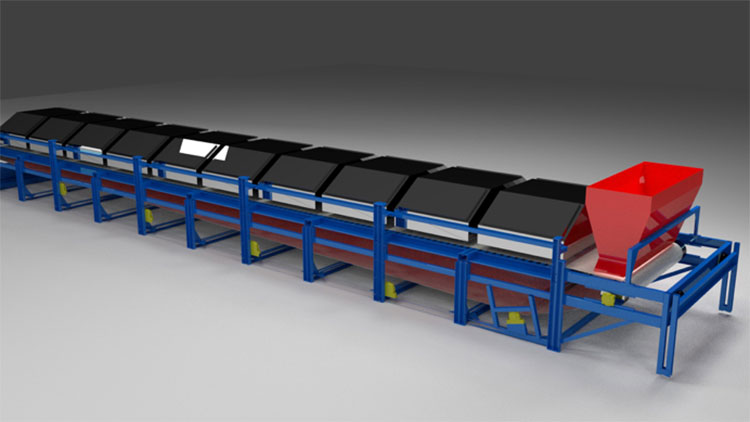
Steel Belt Drying (SBD) Technology
CX-PSS Steel Belt Dryer (SBD™) is a simple dryer, using woven endless steel belt. It is used to dry and dewater minerals without the creation of dust, and at the maximum possible efficiency. The CX-PSS SBD has been successfully installed as an alternative to conventional rotary kiln dryers (typically using gas) on the following products:
- Iron ore and coal fines
- Kimberlite (diamond) concentrates
- Precious and base metal concentrates
- Phosphate concentrates
- Molybdenum concentrates
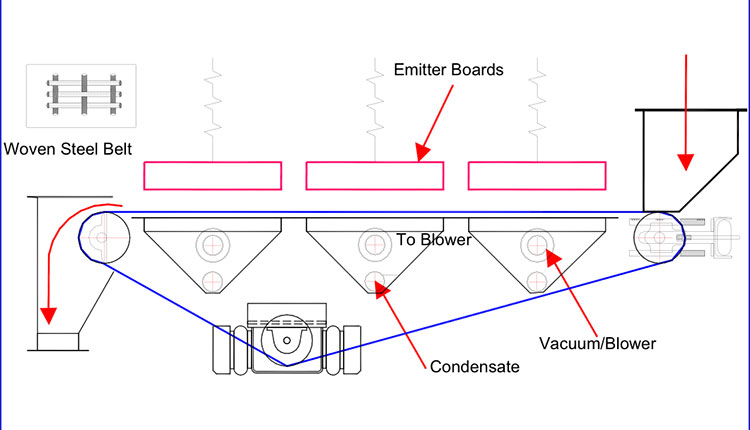
A typical steel belt has a nominal aperture of 200 microns and is joined using a clipper joint (pin seam). The belt circulates in linear motion around a set of pulleys using positive bending only. The belt is driven by a drive pulley, which drives the belt, aligned by the tracking pulley, and tensioned by the tail pulley. The vacuum boxes are situated inside the steel belt underneath the horizontal path of the steel belt.
To track the belt, the tracking roller on the belt return is pivoted on “spherical” bearings. The tracking roller is controlled via a Camtac tracking valve using a pneumatic bellow system for dynamic adjustment when in operation.
The CX-PSS SBD can be manufactured with up to a 3.0 metre belt width, and a 168 kW/m2 array power.
CX-PSS SBD-MIR Special Features
The steel belt dryer can accept feed materials as high as 30% w/w moisture, and can efficiently dry material to as low as 1% w/w moisture.
The feed hopper accepts and spreads the material across the belt evenly to the specified bed height. Screw extrusion can also be used to maximize energy absorption and drying efficiency.
Steel belts are unaffected by variances in temperatures up to 750ºC and can easily accept high temperatures unlike normal plastic or material belts would stretch, or deform.
CX-PSS steel belts are custom fabricated for each project, and are selected for appropriate aperture size, depending on the relative coarseness or fineness of the product.

Medium Wave Infrared Radiation
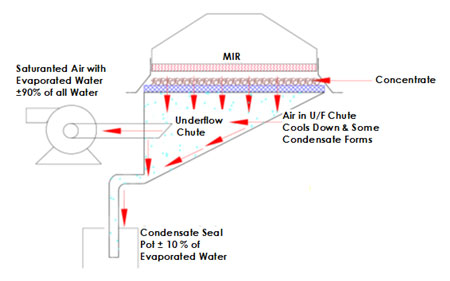
The CX-PSS SBD’s MIR section consists of Medium Wave Infrared Radiation (MIR) emitters mounted on ceramic fibre-boards. The emitted energy heats the water molecules, which subsequently reduce their surface tension and overcome molecular bonding with the substrate. The negative pressure created by the vacuum removes the moisture, away from the emitters, and assists with the energy transfer into the substrate.
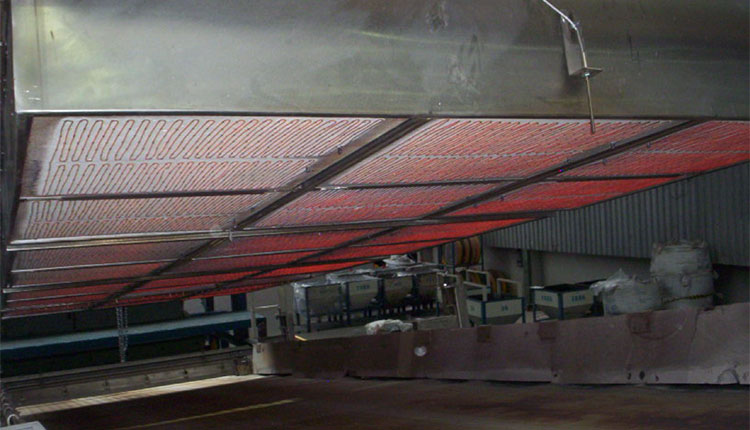

The emitters are fitted inside a stainless steel “array” or otherwise known as “emitter bank”. The sides are raised to accept a 5mm clearance between the hood and the belt.
The product is subjected to 60 – 70% MIR power (36 – 42 kW/m²) which is supplied at power density of 60 kWh/m² (100% power). The emitters are adjustable in height above the substrate. The evaporation of moisture accelerates as the substrate heats up to approximately 90 – 100ºC by which time the moisture content in the substrate is below the free moisture target.
MIR Under Vacuum Concept
When a vacuum is placed at a surface of a substrate, causing air to be drawn through the substrate, the moisture removal efficiency is further enhanced due to:
• The total surface area of the substrate, exposed to the air being is greatly increased by including inner surfaces and both top and bottom surfaces;
• The reduced pressure at the substrate surface where the vacuum is applied – this causes expansion of the air, and consequently a greater capacity for moisture removal;
When heat energy is applied however, the entire process is accelerated because energy is absorbed (not from the ambient material and air as this is normally well below the temperature of the heat source) to heat the substrate and the contained water to the point of boiling, supplying latent energy for change of state to a vapour.
Unique SBD Benefits
Simple to operate
Very economical – low OpEx
Very easy to maintain
Low maintenance costs
Stop/start under full load
1 minute to full production
No product breakage
Condensate water recovery
Instant shut down
The combination of SBD and MIR technologies have resulted in an extremely energy efficient system of between 40 – 70%.
Results obtained through testwork using the systems in combination indicates a coefficient of performance far higher than unity.
Screw Extrusions
CECMS can also supply pin-mixers and extruders that can be used for preparation of granules that have a higher energy absorption. In combination with a binder, this technology can be used to form hard, water-proof extrusions that do not saturate and can be easily handled for transport in wet environments.
Share this Page